What is a wart? We will analyze the causes of occurrence, diagnosis and treatment methods in an article by a dermatologist with 37 years of experience.
Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
Wartsare irregular benign benign skin lesions in the form of a local overgrowth of the upper layer of skin (epidermis) with papules (nodules) or plaques.
The incidence of warts in adults is 7-12%, in school-age children - up to 10-20%.
Warts are very similar to other skin growths. Usually a person can not accurately determine the disease alone, so a dermatologist should be consulted to make a diagnosis.
Human papillomavirus is the cause of warts. The type of virus affects the type of warts that can develop. Thus, each type of human papillomavirus infects tissue at the localization that is most characteristic of it.
| HPV type | Preferred location |
Wart types |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Feet, knees, palms, hands, fingers |
Plantar and palm warts, rarely simple warts |
| 2, 4 | Hands, fingers, knees, less often - feet |
Simple warts, occasional plantar, palmar and mosaic warts |
| 3, 10 | Shins, hands, face | Flat warts |
| 7 | Hands, fingers | Butcher warts |
| 5, 8, 9, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24 |
Face, arms, foreleg |
Epidermodysplasia verruciform |
Viral infection usually occurs through contact - with direct contact between infected and healthy skin (for example by shaking) or indirectly (through railings, toys, etc. ). Therefore, you can become infected with the human papillomavirus, which causes warts, in a wide range of places - in public transport, at school, at work, at home, in places with high contact and a humid environment (swimming pools, saunas, gyms). Minor trauma to the epidermis, through which viruses enter, as well as inflammation of the skin, contribute to infection.
Also contributes to the occurrence of warts:
- immunodeficiency (including HIV infection);
- hot and humid environment;
- the need for professional contact with meat and fish ("butcher warts").
Some types of human papillomavirus are transmitted from parents.
But amphibians and frogs, despite the horror stories we so often fear in childhood, can not be infected - this is one of the most popular myths about this disease, which has no basis.<. x / p>
If you find similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not medicate yourself - it is dangerous for your health!
Wart symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the type of wart.
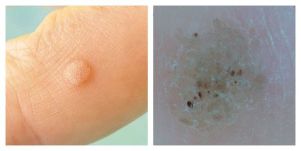
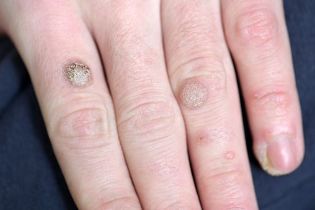
Common wart:
- Round dense papule with normal color, 1-10 mm and larger.
- The surface of the papule is covered with cracks, layers.
- If the papule is on the finger, the printout disappears and is distorted. The same goes for the palm drawing.
- Simple warts are placed either individually or in several pieces - they usually appear in places with the greatest damage (hands, fingers, knees).
- When viewed with a dermatoscope, your doctor may see small brown dots - thrombosed (clogged) capillaries. Patients often refer to these points as "roots". This is a main sign of a doctor: it can be used by a dermatologist to distinguish a wart from other similar diseases (for example, molluscum contagiosum and keratoma).
Plantar (horny) wart:
- The most important symptom that usually causes a patient to see a doctor is pain when pressing and walking.
- Such warts are usually located on the feet.
- When contacting a doctor, there is usually a keratinized, uneven plaque of the usual color visible, although in the first stage one can see a smooth, smooth papule. In keratinization, the capillaries can only be seen if the keratinized layer of the skin is removed.
- The skin on the sole is distorted.
- Plantar warts are usually solitary, but there are also 2-6 warts;
- These warts are often confused with corn (especially dry) - this is the description of the problem that patients usually see.
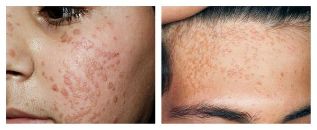
Flat (ung) warts:
- It looks like a round, clear, smooth papule with normal, pink or brownish color, 1-5 mm in size.
- Appears on hands, shins, very often on face.
- There are always several such warts - they are placed in groups.
Epidermodysplasia verruciform (senile wart):
- Large, round, several confluent neoplasms of normal, pink or brown color.
- Most often appears on face, arms, front torso.
- Can be confused with keratoma, shingles and skin cancer.
Wort pathogenesis
Once inside the body, the human papillomavirus can be in a latent state for a long time - a person usually does not even know of its existence. When factors that are beneficial to the virus appear, it begins to "multiply" in the epithelium, leading to tissue changes.
Unlike other viruses, the human papillomavirus does not destroy the cells in the epithelium itself - they die on their own, naturally, in the process of keratinization and flaking.
Local factors and the state of the immune system affect the spread of infections. For example, people with HIV infection or a kidney transplant are more likely to develop warts. In addition, these neoplasms are often difficult to treat. With normal immunity, the virus does not affect the deep layers of the skin, so many people get warts on their own after a few months.
The most important step in the occurrence of warts is the acceleration of the rate of cell division and growth by the virus. This rapid metabolism leads to thickening of the skin layers. As the tissues grow in a specific, small area, a tuber called a wart appears.
Classification and developmental stages of the wart
There is no generally accepted classification of warts. However, there are several common varieties:
- The common wartis the most common type (70% of warts are just them). Such neoplasms are not felt and only cause aesthetic discomfort to a person.
- Plantar warts- appear on the soles of the feet, are painful, therefore require treatment. Skin trauma due to uncomfortable, tight sparkles shoes contribute to the development of such a wart.
- Flat warts- occur more often in young people, adolescents. This is due to the unstable hormonal background in young people affecting the whole body. Usually flat warts are almost invisible.
- Senile warts- typical of the elderly. They often appear on the part of the body that is covered with clothing but can occur on the face and hands. If there is no discomfort, such warts should not be treated - healing in older people can be much slower than in younger people due to a slow metabolism.
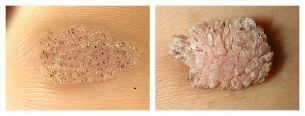
Other authors distinguish several more from these types of warts:
- Mosaic warts(HPV 2, 4) - neoplasms on palms and soles. They are similar to the focus on hyperkeratosis, ie. thickening of the stratum corneum (usually in the forefoot), covered with deep cracks.
- Cystic warts(HPV 60) are a very rare type of neoplasm of the foot. It is a soft knot with cracks. When opened, a white-yellow discharge, corresponding to curd.
- Filiform wartsare thin cane growths near the mouth, nose or eyes.
- Butchery Warts(HPV 7) - Appears on the hands and fingers of people who are in constant contact with meat and fish. Presented as hypertrophied neoplasms similar to cauliflower, but of normal color.
In addition, types of warts are distinguished depending on their location.
So anogenital warts - tumor-like neoplasms that occur on the genitals (especially the places where skin transitions to the mucosa) are a common disease. They are usually caused by HPV types 6 and 11.
Complications of the wart
The main reason why patients with warts go to the doctor is an aesthetic defect that can affect the patient's quality of life, his self-confidence and develop a lot of complexes. Complications can also include cracks in the surface of the wart and the addition of infection, and in some types of warts, soreness during walking.
Skin warts do not usually degenerate into malignant neoplasms, they are quite harmless, but in very rare cases, such a complication can still occur in people with suppressed immune systems.
Other complications occur when trying to remove neoplasms alone. In this regard, inflammation and aesthetic defects may occur in the form of scars, as well as the further spread of the virus through the skin, due to which a person in the morning after self-removal of a wart may wake up with several new ones.
Remember that under a figure of a wart can hide a completely different disease, which can not be determined without the advice of an experienced doctor.
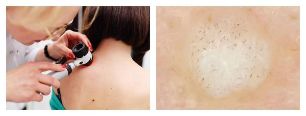
Wart diagnosis
Usually, an examination (clinical picture) and medical history (medical history) are sufficient to make a diagnosis.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may perform a histological examination - the examination of cells in the neoplasm.
It is very important to make a differentiated diagnosis - to distinguish warts from other diseases. For example,common wartsshould be distinguished from the following diseases:
- Molluscum contagiosum- occurs more often on the body and genitals, less often on the hands and feet. It is a hemisphere with impressions on the surface; when pressed from the sides, a whitish "gruel" is released.
- Epidermal verrucous nevus- often lonely, a person has since birth. It rises above the surface of the skin, often covered with hair.
- Basalioma- a tumor in the form of a roll of nodules, covered with a crust in the middle. Typically for the elderly.
Palmar plantar wartsmust be distinguished from the following diseases:
- Keratoderma- large areas of keratinization and inflammation of the skin. No coagulated capillaries.
- Palmar-plantar syphilis- multiple painless neoplasms, skin folds along the periphery. Syphilis has a positive reaction
- Maize- usually painless, can only cause pain when pressed vertically.
The doctor must also differentiate other types of warts from a number of diseases. If another pathology is suspected, he may prescribe additional diagnostics (for example, detection of antibodies to viruses, CT or MRI).
Warts treatment
Warts are treated for aesthetic purposes and to improve the patient's quality of life. It can only be prescribed by a doctor after an examination and an accurately diagnosed diagnosis. Independent attempts to get rid of a wart are unacceptable, as a patient without medical training and the necessary equipment is not able to accurately determine the disease, and complications after such a "treatment" occur much more often than improvement.
There are several ways to treat warts. All are usually performed under the supervision of a doctor, and some of them - only in the treatment room at the clinic.
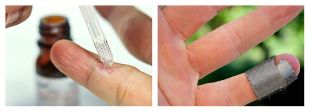
Chemical cure
Milk salicyl colloidion and salicyl patch are used to get rid of warts. The percentage of drugs and the method of their use (long-term use of patches, applications, etc. ) depends on the prevalence and localization of the neoplasm.
Solutions of zinc and 2-chloropropionic acid can also be used. In this case, a chemical composition is applied to the pretreated surface, which is left on the wart until the color changes (depending on the type of wart). The procedure is repeated several times after 7, 14 and 21 days. Before each procedure, the tissue is removed mechanically.
Another chemical method is a combination of nitric acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid, lactic acid and copper nitrate trihydrate. In this way, only relatively small neoplasms are treated - up to 5 mm. The solution is also left to change the color of the wart. After 3-5 days, the patient comes to a follow-up appointment, if necessary, he is prescribed another procedure in 1-4 weeks.

Cryodestruction
This method consists of freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen: the moist tampon is pressed against the damaged skin (with collection of the surrounding tissue by a few mm) for 1-5 minutes. Some lesions require multiple treatments at four-week intervals to destroy.
The main disadvantages of cryodestruction are its painfulness and delayed effect compared to other methods, where only one procedure is often sufficient for removal.
Electrocoagulation
Under the influence of an electric current, the wart is removed in layers. Such an operation is performed under local anesthesia
This method is more effective than cryodestruction, but it has a significant drawback: electrocoagulation often leaves scars at the site of wart removal. For those patients who seek to correct a cosmetic defect,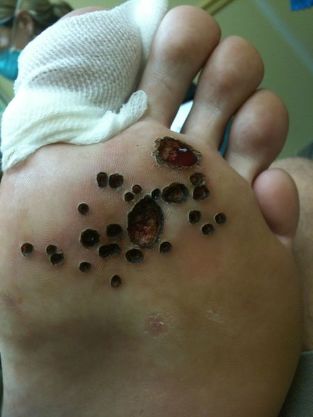 this method is not the most suitable.
this method is not the most suitable.
Laser destruction
The laser also removes layers of warts. The light guide comes in contact with the skin from several seconds to three minutes, depending on the size. Then the crust that appears is cut out and the bottom of the wound is treated again with a laser. The patient is then instructed in how to handle the wound. The operation itself is performed under the influence of local anesthesia.
Radiowave Surgery
Radiowave surgery is one of the most modern and gentle methods to remove some benign neoplasms, including warts.
The method is based on generating electromagnetic waves with different frequencies: from 100 kHz to 105 MHz. During the procedure, the tissues resist the passing waves, and therefore molecular energy is released in the cells that heat the skin. Under the influence of heat, the cells actually evaporate - a nice cut is obtained. At the same time, no mechanical forces are exerted on the affected tissue.
Advantages of this method:
- security;
- fast wound healing;
- good cosmetic effect - scars and scars are excluded;
- Relative Pain Relief - Local Anesthesia Used Before Mini-Surgery;
- exclusion of secondary infection due to automatic disinfection of the electrode when the device is switched on.
The effectiveness of this method is recognized worldwide, but it is quite difficult to find a clinic that uses the method of radiowave surgery.
Which treatment method to choose
All of the above methods have several disadvantages:
- For the first few weeks, the operated area looks unattractive - crust, darker tissue. This should be taken into account if the warts are on visible parts of the body (for example on the face).
- Unpleasant odor and some degree of pain during surgery.
Additionally, each of these methods has contraindications that you need to find out about in an initial consultation with a dermatologist.
But the biggest drawback isthere is a high probability of recurrence, especially if the warts were widespread and extensive. With each of these methods, doctors do not fight the root cause of the disease, but with its consequences, since todayhuman papillomavirus can not be cured.
Therefore, therapy is aimed at:
- or destruction of neoplasms that appear at the site of introduction of the virus;
- either to stimulate an antiviral immune response;
- or a combination of these methods.
Destructive treatment methods are often used. Their efficiency reaches 50-80%.
Childhood is usually not a contraindication to surgical treatments. Therefore, many of them (including radiowave surgery) are also used to treat warts in children. An exception is chemical removal of warts due to the possibility of side effects on the drug.
What to do after the operation
After one of these surgeries, be sure to follow your doctor's recommendations.
After removal of the tumor using any of the methods presented, the doctor usually prescribes the treatment of the removal site. It is forbidden to remove the "crust" on its own, wet the wound and expose it to direct sunlight.
If a patient is constantly suffering from warts, he should consult an immunologist - this may require drug therapy, which will increase the resistance of immunity to the manifestations of the human papillomavirus.
Forecast. Prevention
If the patient does not have an immune deficiency, the warts may go away on their own, but this will take a long time - from several months to several years. Thus, in 65% of cases, warts regress independently within two years. If the wart is still in place after two years, it is recommended to remove it. It is recommended to remove several growths immediately.
With normal immunity and a correctly chosen removal method (depending on the size and type of wart) it is possible to remove pathogenic tissue and achieve a good cosmetic effect. With reduced immunity and other predisposing factors, the remaining human papillomavirus in the body causes relapse.
There is no specific disease prevention. But is infection so inevitable?
You can reduce the likelihood of a virus by following a few rules:
- Avoid walking barefoot in public places where there is a possibility of skin damage and viral infection (swimming pools, public showers, gyms).
- Choose high-quality footwear, change it often. Try to keep your feet dry. Heat and moisture are excellent breeding grounds for human papillomavirus.
- To avoid periungual warts, go to a certified manicure nail technician and make sure they use sterile instruments.
To prevent anogenital warts, according to the WHO (World Health Organization), a quadrival vaccine against human papillomavirus is also extremely effective. There are currently no vaccines available to prevent other types of warts.
If you find a wart, do not try to cauterize, cut or pick it by yourself - this way you can contribute to inflammation and further spread of the virus along the skin. After such a "removal", instead of a wart in the morning, you can wake up with ten.














































































